
Introduction:
Welcome to our intermediate English learning lesson on sentence structure! Understanding the components of a sentence is fundamental for constructing clear and grammatically correct sentences in English. In this lesson, you will explore the essential elements of sentence structure, including the subject, predicate, and object. This knowledge is crucial for developing your writing and speaking skills, allowing you to communicate more effectively in English. Let's dive into the intricacies of sentence construction!
Lesson Content:
In this lesson, you will learn about sentence structure in English.
Explanation:
Understanding how sentences are structured in English is vital for clear communication. Sentences are composed of three main components: the subject, predicate, and object. Here, we will break down each component and provide examples to help you grasp their roles and how they interact within a sentence.
Subject:
The subject is the part of the sentence that performs the action or about which something is stated. It tells us who or what the sentence is about.
Definition: The subject is the noun, pronoun, or noun phrase that indicates what the sentence is about or who/what performs the action.
Examples: In the sentence "The cat sleeps," "The cat" is the subject because it is the entity performing the action of sleeping.
Predicate:
The predicate contains the verb and provides information about the subject. It explains what the subject is doing or what is happening to the subject.
Definition: The predicate is the part of the sentence that tells us what the subject does or what is done to the subject. It includes the verb and any accompanying words that provide more detail.
Examples: In the sentence "The cat sleeps," "sleeps" is the predicate because it describes the action that the subject (the cat) is performing.
Object:
The object is the part of the sentence that receives the action of the verb or completes the meaning of the predicate. It provides additional details to give a complete sense of the action.
Definition: The object is the noun, pronoun, or noun phrase that receives the action of the verb or is affected by it.
Examples: In the sentence "She eats an apple," "apple" is the object because it is receiving the action of being eaten.
By understanding and identifying these components, you will be able to construct more complex and grammatically correct sentences, improving your overall communication skills in English.
Introduction: Welcome to our intermediate English learning lesson on sentence structure! Understanding the components of a sentence is fundamental for constructing clear and grammatically correct sentences in English.
In this lesson, you will explore the essential elements of sentence structure, including the subject, predicate, and object.
This knowledge is crucial for developing your writing and speaking skills, allowing you to communicate more effectively in English.
Let's dive into the intricacies of sentence construction! Lesson Content: In this lesson, you will learn about sentence structure in English.
Explanation: Understanding how sentences are structured in English is vital for clear communication.
Sentences are composed of three main components: the subject, predicate, and object.
Here, we will break down each component and provide examples to help you grasp their roles and how they interact within a sentence.
Subject: The subject is the part of the sentence that performs the action or about which something is stated.
It tells us who or what the sentence is about.
Definition: The subject is the noun, pronoun, or noun phrase that indicates what the sentence is about or who/what performs the action.
Examples: In the sentence "The cat sleeps," "The cat" is the subject because it is the entity performing the action of sleeping.
Predicate: The predicate contains the verb and provides information about the subject.
It explains what the subject is doing or what is happening to the subject.
Definition: The predicate is the part of the sentence that tells us what the subject does or what is done to the subject.
It includes the verb and any accompanying words that provide more detail.
Examples: In the sentence "The cat sleeps," "sleeps" is the predicate because it describes the action that the subject (the cat) is performing.
Object: The object is the part of the sentence that receives the action of the verb or completes the meaning of the predicate.
It provides additional details to give a complete sense of the action.
Definition: The object is the noun, pronoun, or noun phrase that receives the action of the verb or is affected by it.
Examples: In the sentence "She eats an apple," "apple" is the object because it is receiving the action of being eaten.
By understanding and identifying these components, you will be able to construct more complex and grammatically correct sentences, improving your overall communication skills in English.
|
|

SubjectSubjectThe first part in the simple English sentence. In grammar, the subject is the noun, pronoun, or noun phrase that performs the action of the verb or is described by the verb. It is typically located at the beginning of a sentence and indicates who or what the sentence is about. |

verbverbthe action or state of being in the English sentence. |

predicatepredicatethe part of the sentence that contains the verb and provides information about the subject. |

objectobjecthe part of the sentence that receives the action of the verb. |

catcat |

dogdog |

JohnJohn |

ParisParis |

SheShe |

HeHe |

TheyThey |
WeWe |

ItItThe pronoun "it". is used to refer to a previously mentioned or easily identifiable noun that is typically inanimate or not personified. It's often employed to represent objects, animals, or concepts. |

The catThe cat |

A dogA dog |
John and MaryJohn and Mary |

The childrenThe children |

My friendMy friend |
My sisterMy sister |
The teacherThe teacher |

The bookThe book |

The carThe car |

Our houseOur house |
The presidentThe president |

The sunThe sun |

A birdA bird |

This computerThis computer |

PredicatePredicate |
sleepssleeps |

eatseats |

playsplays |

isisThe word "is". is a form of the verb "to be". in the present tense, specifically used with third-person singular subjects, such as "he," "she," or "it." It indicates a state of existence, identity, or a characteristic of the subject. |

amamThe word "am". is a form of the verb "to be". in the present tense, specifically used with the first-person singular subject, "I." It indicates a state of existence, identity, or a characteristic of the speaker. |

areareThe word "are". is a form of the verb "to be". in the present tense, specifically used with plural subjects, such as "they are" or "we are". It indicates a state of existence, identity, or a characteristic of the subject. |
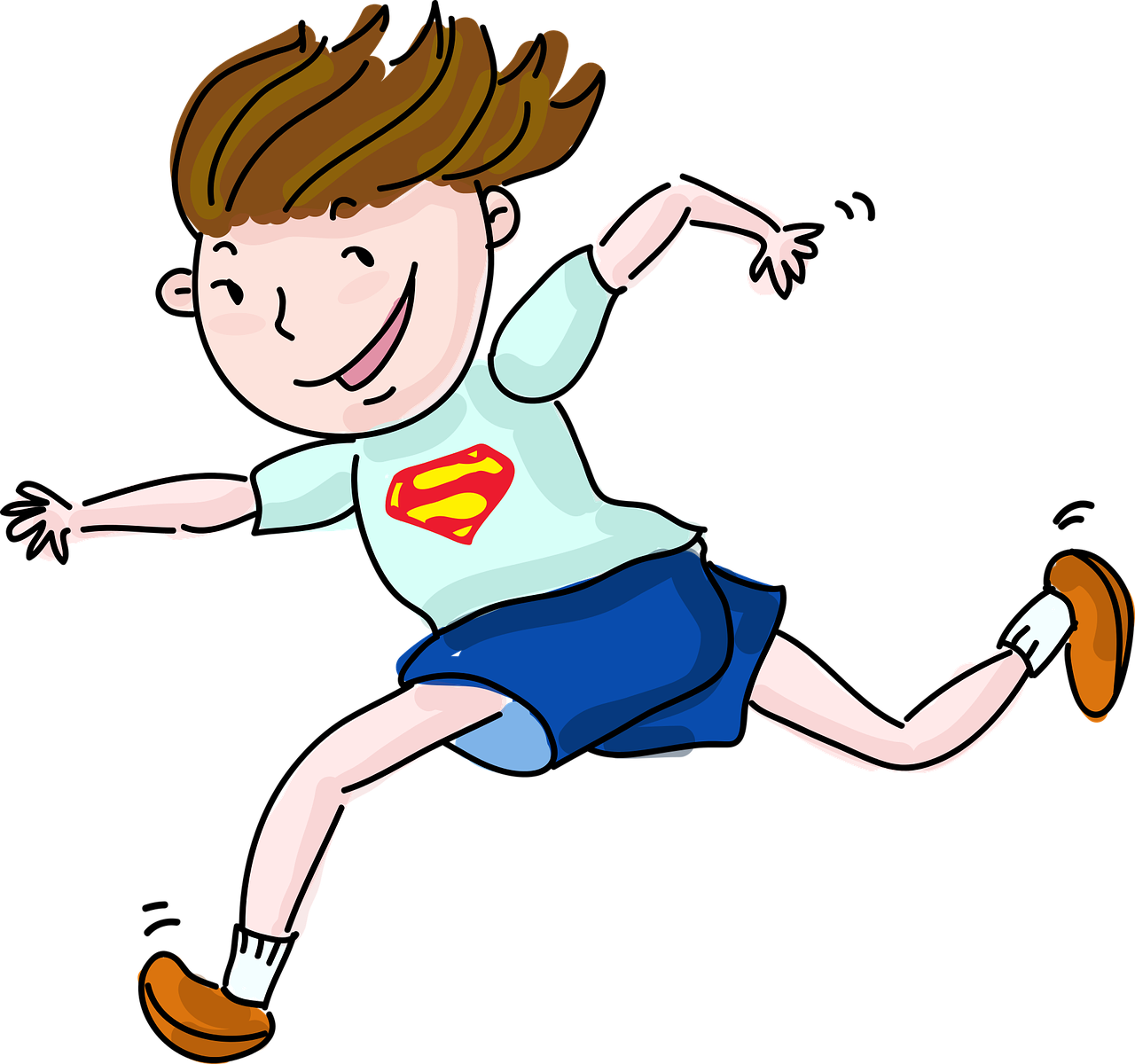

runsrunsThe verb "runs" typically refers to the action of moving swiftly on foot, or operating or functioning, such as a machine, organization, or system. |
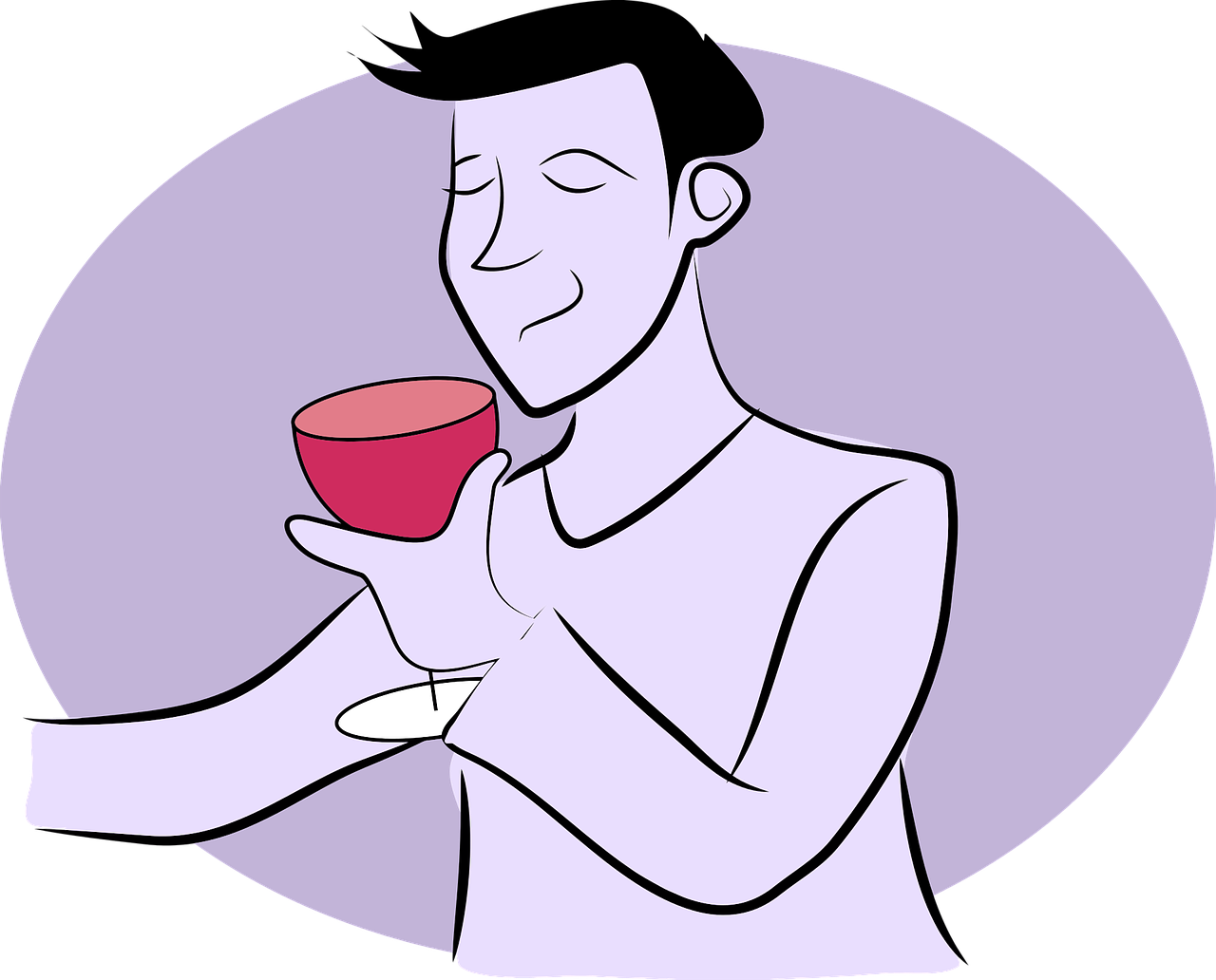

drinksdrinksThe verb "drinks" typically describes the action of consuming liquid, usually referring to the act of ingesting a beverage such as water, juice, or coffee. |
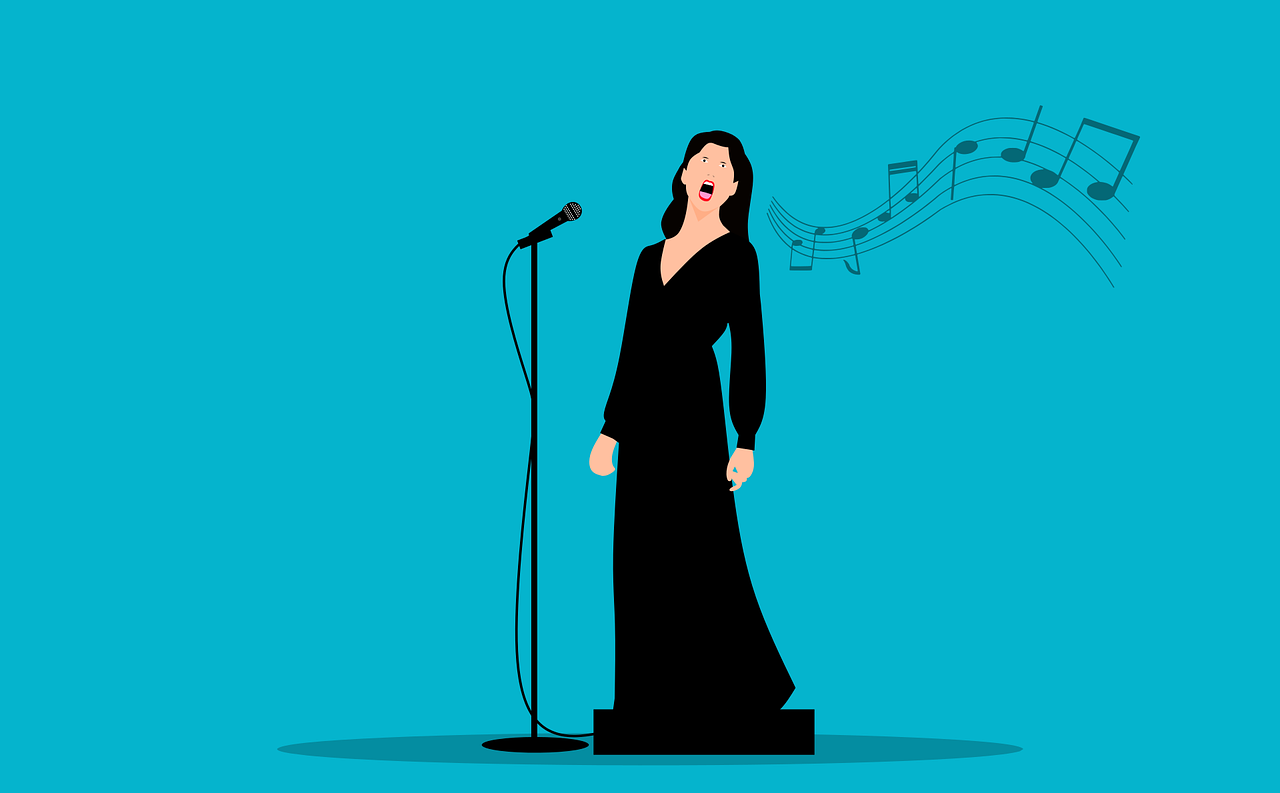

singssings |
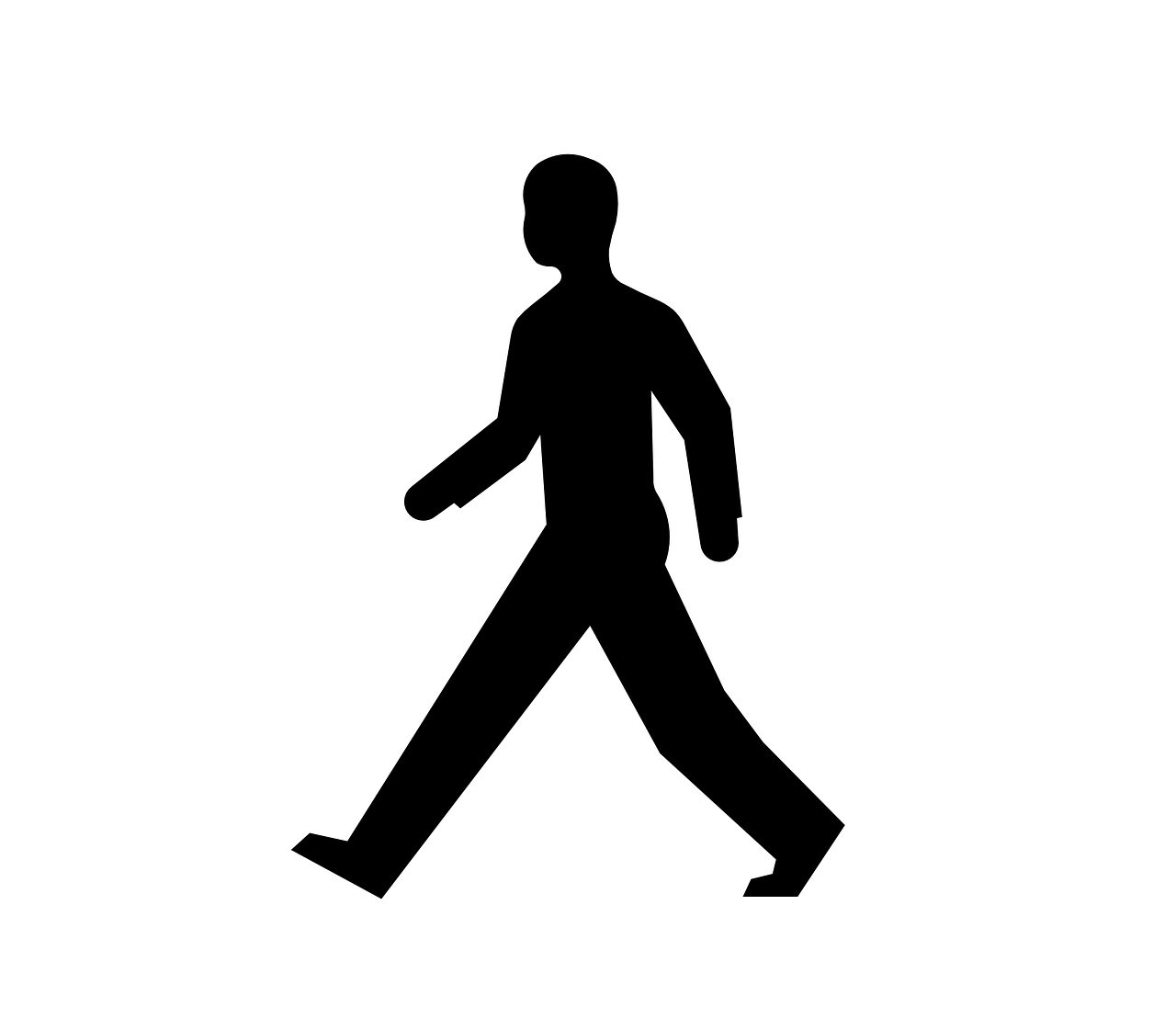

walkswalks |

jumpsjumps |

writeswrites |

listenslistens |

speaksspeaks |
teachesteaches |

studiesstudiesThe verb "studies" generally means the act of examining, researching, or learning about a subject in a systematic and focused manner. |

worksworks |

swimsswims |

dancesdancesThe verb "dances" refers to the action of moving rhythmically to music, typically involving coordinated movements of the body and limbs. |
fliesflies |

drivesdrivesThe verb "drives" typically refers to the action of operating a vehicle, guiding it along a route or path, usually with the intention of reaching a destination. |

cookscooksThe verb "cook" describes the action of preparing food by applying heat, often in various methods such as baking, frying, boiling, or grilling. |

sleepssleeps |

laughslaughs |

criescriesis the present tense form of the verb "cry." It typically describes the action of shedding tears or making loud sounds expressing distress or pain. |

ObjectObjectIn grammar, when "object" appears as the last part of a sentence, it usually refers to the noun or pronoun that receives the action of the verb or shows the result of the action. It can be either a direct object, receiving the action directly, or an indirect object, affected by the action indirectly. |

appleapple |
bookbook |

ballball |

cakecake |
pencilpencil |

catcat |

dogdog |

birdbird |
fishfish |
rabbitrabbit |

chairchair |
bedbed |

couchcouch |
deskdesk |

computercomputer |

phonephone |

TVTV |
radioradio |

cameracamera |

carcar |

bikebike |

planeplane |

boatboat |

traintrain |

Examples of sentencesExamples of sentences |

She eats an appleShe eats an apple |

He plays soccerHe plays soccer |
They are happyThey are happy |

John is tallJohn is tall |

Paris is beautifulParis is beautiful |

I run quicklyI run quickly |

She sings beautifullyShe sings beautifully |

The sun setsThe sun sets |

We study nowWe study now |

They play thereThey play there |

He reads a bookHe reads a book |

The cat sleepsThe cat sleeps |

He writes a letterHe writes a letter |

They watch TVThey watch TV |
We laugh loudlyWe laugh loudly |

readsreads |
tabletable |
Congratulations! You have now learned the basic components of sentence structure in English.
By understanding subjects, predicates, and objects, you can create more complex and accurate sentences.
Keep practicing to enhance your grammatical skills and become more proficient in English.